TLA PlugFest
 In June 2022 the Advanced Distributed Learning Initiative held their first PlugFest in over a decade. This PlugFest was centered around the Department of Defense’s Total Learning Architecture and the role of the Experience API (xAPI) in its success. The DoD’s Total Learning Architecture (TLA) model is an ambitious program that has been on the horizon since the inception of xAPI. The goal of the TLA is to tie the DoD’s various learning applications, testing/qualification programs, human performance systems and other personnel management services together to track a soldier’s competence across their career – from taking the ASVAB to post-service transition.
In June 2022 the Advanced Distributed Learning Initiative held their first PlugFest in over a decade. This PlugFest was centered around the Department of Defense’s Total Learning Architecture and the role of the Experience API (xAPI) in its success. The DoD’s Total Learning Architecture (TLA) model is an ambitious program that has been on the horizon since the inception of xAPI. The goal of the TLA is to tie the DoD’s various learning applications, testing/qualification programs, human performance systems and other personnel management services together to track a soldier’s competence across their career – from taking the ASVAB to post-service transition.
There are many benefits to having this holistic understanding of a service members’ abilities. Having an inventory of skills and competences allows for the nimble assembly of work teams with the right experience for the job. Understanding someone’s current abilities can be used to support adaptive and personalized training paths eliminating redundancy and cost. A person’s past performance can be used to help guide career planning and identify knowledge-gaps that must be closed for advancement. But with thousands of systems across the armed forces around the world and millions of pieces of content, how does the TLA make this happen? TLA PlugFest provides some answers.
So, what is PlugFest? As you can imagine there are a number of parallel development efforts all converging to support the TLA. xAPI itself is going through IEEE standardization. cmi5, the replacement standard for SCORM, has matured and a conformance suite developed by Rustici Software. Eduworks’ Competency and Skills Software (CaSS) is being used to develop a library of skills needed for success. At the same time, Deloitte is collecting learning metadata as part of the Enterprise Course Catalog with the goal of being able to cross-reference learning activities and the competencies those activities support across all branches of the military.
With all these moving parts, PlugFest gives the government, vendors and suppliers a chance to work together, discuss each other’s needs and ensure interoperability. As part of each hands-on session, attendees are encouraged to bring their own projects or data to test. New products are explored and attendees give feedback on their use. At the end of PlugFest, everyone received a take-away tool kit to continue exploring back on the job.
Day 1
Day one of the TLA PlugFest started off with Brent Smith, R&D Principal for the ADL initiative. Brent led us through the evolution of the Total Learning Architecture over the past five years. The ADL is supporting four separate IEEE Standards as the foundation of the TLA:
- The Experience API – IEEE 9274.1
- Standards for Enterprise Learner Records – IEEE P2997
- Standards for Learning Metadata – IEEE P2881
- Reusable Competency Definitions – IEEE 1484.20.1
These four standards govern the TLA Data Pillars where xAPI is sent to Transactional Learning Record Stores, which standardize the data and forwarded it to Authoritative Learning Record Stores. s. Learner Profiles are created based on data defined in the Enterprise Learner Records standard. The Enterprise Course Catalog uses Learning Metadata to cross-reference learning events, providers and the skills those events teach. All of this data can then be used by the Competency Registry to recommend learning plans, to drive adaptive content and to ensure needed skills can be deployed easily.
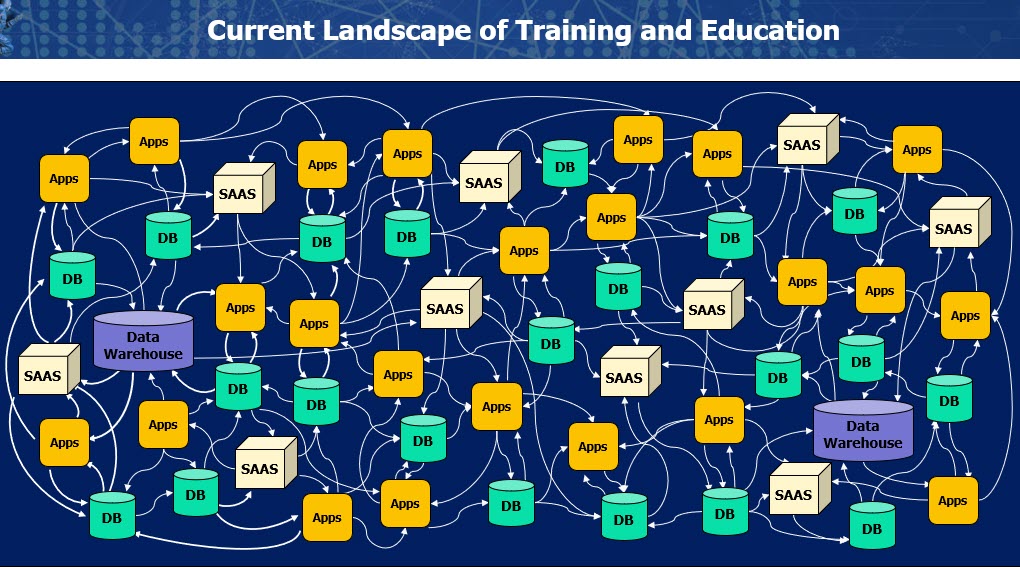 Brent shared the current state of Training and Education in the military as decentralized and siloed. The vision moving forward is still a decentralized learning model so that different locations and branches can adapt content to their specific needs while still feeding data to a centralized systems. The ability to centralize all this learning and human performance data hinges on adherence to the standards. It’s the standards that give us the freedom to develop applications, learning record stores and other tools with confidence that they will be interoperable. Of course it’s nice to have an event like PlugFest where we can actually see these tools working together.
Brent shared the current state of Training and Education in the military as decentralized and siloed. The vision moving forward is still a decentralized learning model so that different locations and branches can adapt content to their specific needs while still feeding data to a centralized systems. The ability to centralize all this learning and human performance data hinges on adherence to the standards. It’s the standards that give us the freedom to develop applications, learning record stores and other tools with confidence that they will be interoperable. Of course it’s nice to have an event like PlugFest where we can actually see these tools working together.
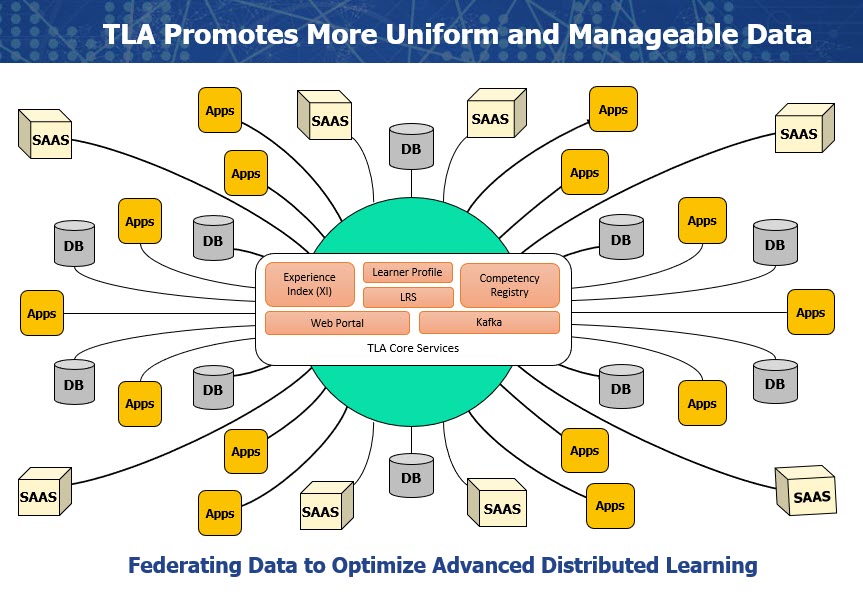
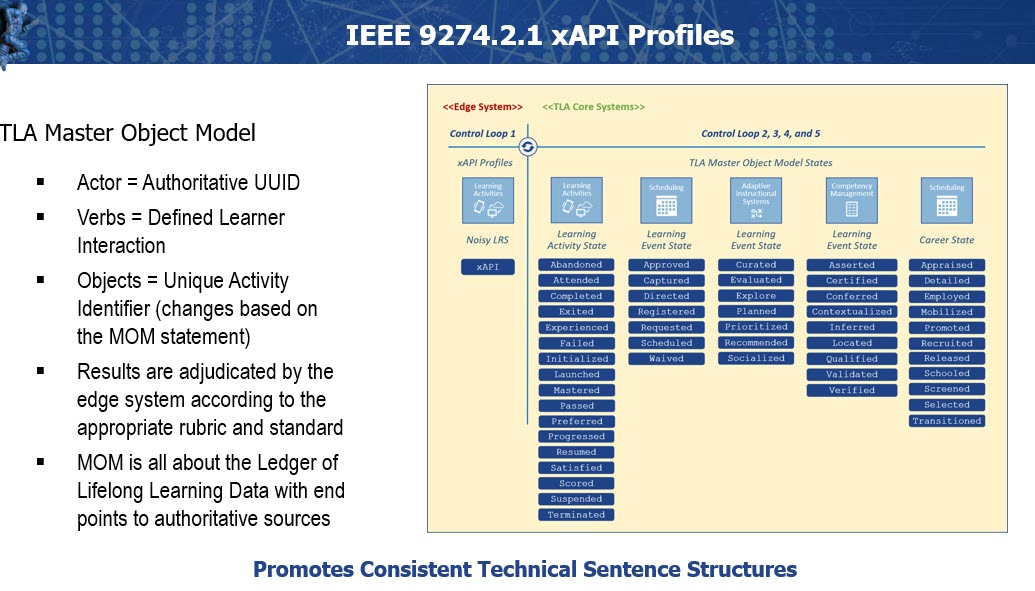
After Brent set the stage for the future of learning across the DoD, Andy Johnson brought us back to the fundamentals of xAPI and why it is needed to help transport and aggregate learning data. Andy went on to discuss how xAPI profiles are guidelines for xAPI in specific use-cases for xAPI. Examples of xAPI profiles include a video profile for recording a student’s use of video in a learning event using xAPI. To ensure semantic interoperability, part of the TLA process to establish a Master Object Model. The purpose of the TLA “MOM” is to provide standard vocabularies to promote consistent data structure. In the image below we can see how xAPI data may be forwarded from a “Transactional” or “Noisy LRS” to an “Authoritative LRS” using established language. Because each verb is uniquely defined the MOM allows the authoritative LRS to provide a ledger of lifelong learning data for students.
For the hands-on element of xAPI basics, new courses were launched sending statements to multiple LRS. LRS providers could then show the visualization possible from the LRS right “out of the box”. This provided a great example of why consistent data is critical for reporting. Yet Analytics gave a demonstration of their application called DATASIM that can create large volumes of xAPI data for testing and developing visualizations. The key to DATASIM’s success is that it does adhere to xAPI profiles so you can ensure quality statements, delivered in the proper order while avoiding all personally identifiable information in the LRS.
After lunch, the day continued into cmi5, the DoD’s replacement for SCORM using xAPI. Essentially, cmi5 adds rules for xAPI for the use-case where content is launched from a Learning Management System (LMS). xAPI doesn’t require an LMS, for instance a mobile app could send xAPI data directly to an LRS. cmi5 is the profile that extends xAPI’s reach in a consistent way by defining things like move-on criteria, content packaging and course structure. Andy Johnson lead a hands-on activity to transition SCORM and other content to cmi5. LMS providers could then show how their product launched courses and received results. Some attendees even brought samples of their own cmi5 courses to test out!
Day 2
Day two kicked off with competencies. The Competency and Skills Software (CaSS) from Eduworks has been developed to build a standards-based competency framework for use across the DoD. Fritz Ray, Eduwork Chief Technology Officer, is currently working with the US Navy to map competencies across the service. Having this inventory of skills has already allowed for improved response times when assembling rapid-response teams. Ultimately, having a clear understanding of a person’s skills, knowledge and abilities can be used to provide a personalized and streamlined learning experience. Of course, the process of defining competencies, identifying learning resources that can help develop a competency and managing variations can be quite a task. That is where Learning Metadata and the Enterprise Course Catalog come into play.
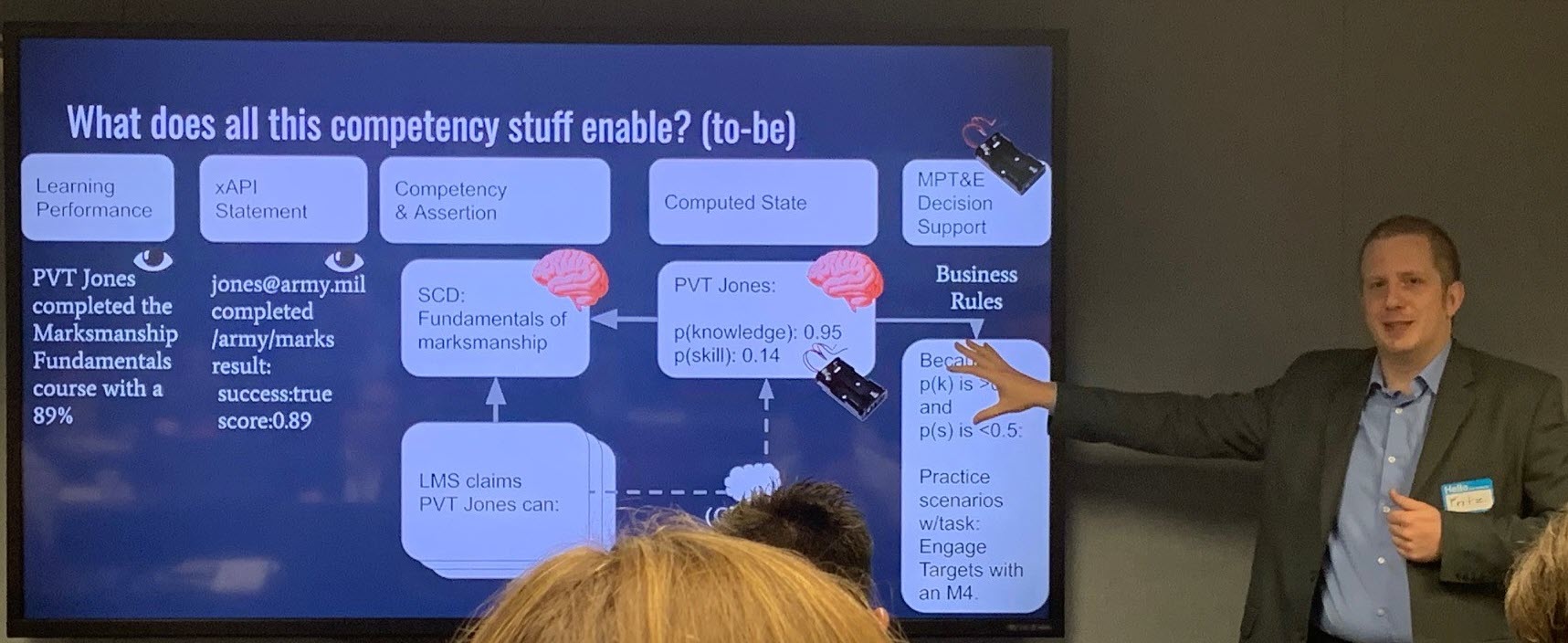
The IEEE has a new draft standard (P2881) on learning metadata. This metadata is housed in the Enterprise Course Catalog developed by Deloitte. Using this metadata we now establish a line of sight across the TLA. Course objectives, the competencies they support, proficiency level, and course equivalencies are searchable and machine readable. With all this information at their fingertips, career counselors can develop a truly learner-centered development plan and even identify opportunities like community colleges offering equivalent courses locally to eliminate travel expense and time over attending a bespoke class at another military base.
Brent and Andy wrapped up PlugFest by stepping back and looking at the TLA holistically again. Shelly Blake-Plock from Yet Analytics discussed two solutions to help support and test the TLA. First is the DATASIM product discussed earlier for creating quality xAPI data at scale. This allows for load testing application confident that the xAPI itself is accurate. xAPIPipe is a statement forwarding tool that accompanies one LRS and forwards statements to another LRS. This automated forwarding helps bring the concept of noisy versus authoritative LRS to reality.
With TLA Plugfest 2022 in the books, it’s clear that the US Department of Defense is taking action to modernize and personalize learning and development across the services. The international adoption of learning standards by the IEEE facilitates this process by establishing guidelines for interoperability. Look to these innovators as systems continue to mature and the data gathered on students can be used to inform career choices. Continue to watch as these tools become more integrated and the ADL drives innovation with its government, private and academic partners.
